
 47:15
47:15
2024-06-28 09:29
![Парсим XML файл python [ часть 3 ]](https://pic.rutubelist.ru/video/e7/15/e715d64d110136bc32fb40e34f3d0100.jpg?width=300)
 7:03
7:03
![Парсим XML файл python [ часть 3 ]](https://pic.rutubelist.ru/video/e7/15/e715d64d110136bc32fb40e34f3d0100.jpg?width=300)
 7:03
7:03
2023-11-27 23:57
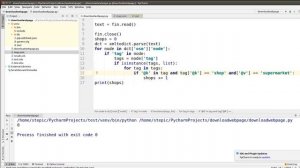
 6:04
6:04

 6:04
6:04
2023-11-30 12:39
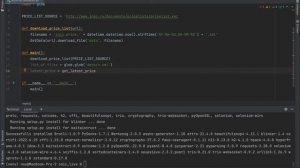
 8:30
8:30

 8:30
8:30
2024-10-23 07:56

 6:35
6:35

 6:35
6:35
2025-09-11 19:58

 14:38
14:38

 14:38
14:38
2025-09-04 14:51
 1:11
1:11

 1:11
1:11
2025-09-22 05:01

 2:32
2:32

 2:32
2:32
2025-08-26 08:30

 55:20
55:20

 55:20
55:20
2025-09-26 19:00
 3:56
3:56

 3:56
3:56
2025-08-26 10:37

 13:20
13:20

 13:20
13:20
2025-09-03 21:34

 57:51
57:51

 57:51
57:51
2025-09-26 11:07

 0:27
0:27

 0:27
0:27
2025-09-23 20:02

 4:06
4:06

 4:06
4:06
2025-09-04 05:51

 4:43
4:43

 4:43
4:43
2025-08-22 11:57

 6:14
6:14

 6:14
6:14
2025-08-22 09:00

 0:49
0:49

 0:49
0:49
2025-09-11 14:43

 13:06
13:06
![Хушнуд - Бевафо ёр (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 5:39
5:39
![Азамат Исенгазин - Мой свет (Премьера 2025)]() 2:47
2:47
![Динара Швец - Нас не найти (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:46
3:46
![Джатдай - Тобою пленен (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 1:59
1:59
![Рейсан Магомедкеримов - Моя мадам (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:28
3:28
![Маша Шейх - Будь человеком (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:41
2:41
![АКУЛИЧ - Красные глаза (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:13
2:13
![UMARO - 1-2-3 (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:52
2:52
![ZIMMA - Город Тает (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:30
2:30
![SHAXO - Пьяница (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:32
3:32
![Аброр Киличов - Тим-Тим (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 4:42
4:42
![Фрося - На столике (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 1:42
1:42
![ZAMA - Глаза цвета кофе (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:57
2:57
![Катя Маркеданец - Мама (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:32
3:32
![Шохжахон Раҳмиддинов - Арзон (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:40
3:40
![Мужик из СИБИРИ (Александр Конев) - Поцелуи осени (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:59
2:59
![Шавкат Зулфикор & Нурзида Исаева - Одамнинг ёмони ёмон буларкан (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 8:21
8:21
![Зульфия Чотчаева - Холодное сердце (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:52
2:52
![Шамиль Кашешов - Когда мы встретились с тобой (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:10
3:10
![Бекзод Хаккиев - Айтаман (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:41
2:41
![Однажды в Ирландии | The Guard (2011) (Гоблин)]() 1:32:16
1:32:16
![Заклятие 4: Последний обряд | The Conjuring: Last Rites (2025)]() 2:15:54
2:15:54
![Диспетчер | Relay (2025)]() 1:51:56
1:51:56
![Плохой Cанта 2 | Bad Santa 2 (2016) (Гоблин)]() 1:28:32
1:28:32
![Бешеные псы | Reservoir Dogs (1991) (Гоблин)]() 1:39:10
1:39:10
![Протокол выхода | Exit Protocol (2025)]() 1:24:45
1:24:45
![Фантастическая четвёрка: Первые шаги | The Fantastic Four: First Steps (2025)]() 1:54:40
1:54:40
![Баллада о маленьком игроке | Ballad of a Small Player (2025)]() 1:42:60
1:42:60
![Богомол | Samagwi (2025)]() 1:53:29
1:53:29
![Терминатор 2: Судный день | Terminator 2: Judgment Day (1991) (Гоблин)]() 2:36:13
2:36:13
![Чумовая пятница 2 | Freakier Friday (2025)]() 1:50:38
1:50:38
![Вальсируя с Брандо | Waltzing with Brando (2024)]() 1:44:15
1:44:15
![Крысы: Ведьмачья история | The Rats: A Witcher Tale (2025)]() 1:23:01
1:23:01
![Дом из динамита | A House of Dynamite (2025)]() 1:55:08
1:55:08
![Отчаянный | Desperado (1995) (Гоблин)]() 1:40:18
1:40:18
![Стив | Steve (2025)]() 1:33:34
1:33:34
![Большое смелое красивое путешествие | A Big Bold Beautiful Journey (2025)]() 1:49:20
1:49:20
![Франкенштейн | Frankenstein (2025)]() 2:32:29
2:32:29
![Цельнометаллическая оболочка | Full Metal Jacket (1987) (Гоблин)]() 1:56:34
1:56:34
![Рок-н-рольщик | RocknRolla (2008) (Гоблин)]() 1:54:23
1:54:23
![Космический рейнджер Роджер Сезон 1]() 11:32
11:32
![Команда Дино. Исследователи Сезон 1]() 13:10
13:10
![Супер Зак]() 11:38
11:38
![Папа Супергерой Сезон 1]() 4:28
4:28
![Синдбад и семь галактик Сезон 1]() 10:23
10:23
![Супер Дино]() 12:41
12:41
![Агент 203]() 21:08
21:08
![Сборники «Умка»]() 1:20:52
1:20:52
![МиниФорс]() 0:00
0:00
![Корги по имени Моко. Защитники планеты]() 4:33
4:33
![Сборники «Простоквашино»]() 1:05:35
1:05:35
![Чуч-Мяуч]() 7:04
7:04
![Псэмми. Пять детей и волшебство Сезон 1]() 12:17
12:17
![Школьный автобус Гордон]() 12:34
12:34
![Отряд А. Игрушки-спасатели]() 13:06
13:06
![Чемпионы]() 7:12
7:12
![Тайны Медовой долины]() 7:01
7:01
![Сборники «Приключения Пети и Волка»]() 1:50:38
1:50:38
![Пакман в мире привидений]() 21:37
21:37
![Мультфильмы военных лет | Специальный проект к 80-летию Победы]() 7:20
7:20

 13:06
13:06Скачать Видео с Рутуба / RuTube
| 256x144 | ||
| 426x240 | ||
| 640x360 | ||
| 854x480 | ||
| 1280x720 | ||
| 1920x1080 |
 5:39
5:39
2025-11-23 13:40
 2:47
2:47
2025-11-19 11:44
 3:46
3:46
2025-11-12 12:20
 1:59
1:59
2025-11-15 12:25
 3:28
3:28
2025-11-20 13:54
 2:41
2:41
2025-11-12 12:48
 2:13
2:13
2025-11-15 12:35
 2:52
2:52
2025-11-14 12:21
 2:30
2:30
2025-11-21 13:20
 3:32
3:32
2025-11-18 12:49
 4:42
4:42
2025-11-17 14:30
 1:42
1:42
2025-11-12 12:55
 2:57
2:57
2025-11-13 11:03
 3:32
3:32
2025-11-17 14:20
 3:40
3:40
2025-11-21 13:31
 2:59
2:59
2025-11-21 13:10
 8:21
8:21
2025-11-17 14:27
 2:52
2:52
2025-11-18 11:48
 3:10
3:10
2025-11-22 12:41
 2:41
2:41
2025-11-17 14:22
0/0
 1:32:16
1:32:16
2025-09-23 22:53
 2:15:54
2:15:54
2025-10-13 19:02
 1:51:56
1:51:56
2025-09-24 11:35
 1:28:32
1:28:32
2025-10-07 09:27
 1:39:10
1:39:10
2025-09-23 22:53
 1:24:45
1:24:45
2025-11-13 23:26
 1:54:40
1:54:40
2025-09-24 11:35
 1:42:60
1:42:60
2025-10-31 10:53
 1:53:29
1:53:29
2025-10-01 12:06
 2:36:13
2:36:13
2025-10-07 09:27
 1:50:38
1:50:38
2025-10-16 16:08
 1:44:15
1:44:15
2025-11-07 20:19
 1:23:01
1:23:01
2025-11-05 19:47
 1:55:08
1:55:08
2025-10-29 16:30
 1:40:18
1:40:18
2025-09-23 22:53
 1:33:34
1:33:34
2025-10-08 12:27
 1:49:20
1:49:20
2025-10-21 22:50
 2:32:29
2:32:29
2025-11-17 11:22
 1:56:34
1:56:34
2025-09-23 22:53
 1:54:23
1:54:23
2025-09-23 22:53
0/0
2021-09-22 21:49
2021-09-22 22:45
2021-09-22 22:07
2021-09-22 21:52
2021-09-22 23:09
 12:41
12:41
2024-11-28 12:54
 21:08
21:08
2025-01-09 16:39
 1:20:52
1:20:52
2025-09-19 17:54
 0:00
0:00
2025-11-24 01:56
 4:33
4:33
2024-12-17 16:56
 1:05:35
1:05:35
2025-10-31 17:03
 7:04
7:04
2022-03-29 15:20
2021-09-22 22:23
 12:34
12:34
2024-12-02 14:42
 13:06
13:06
2024-11-28 16:30
 7:12
7:12
2025-11-21 03:26
 7:01
7:01
2022-03-30 17:25
 1:50:38
1:50:38
2025-10-29 16:37
 21:37
21:37
2024-11-28 17:35
 7:20
7:20
2025-05-03 12:34
0/0

