23:53
23:53
2025-09-21 21:00
 3:56
3:56

 3:56
3:56
2025-08-26 10:37

 5:39
5:39

 5:39
5:39
2025-08-26 13:35

 0:30
0:30

 0:30
0:30
2025-09-17 10:00

 2:32
2:32

 2:32
2:32
2025-08-26 08:30

 14:38
14:38

 14:38
14:38
2025-09-04 14:51

 6:59
6:59

 6:59
6:59
2025-09-22 16:48

 17:27
17:27

 17:27
17:27
2025-09-03 17:00

 2:52
2:52

 2:52
2:52
2025-09-18 18:40

 11:45
11:45

 11:45
11:45
2025-09-01 07:11

 4:43
4:43

 4:43
4:43
2025-08-22 11:57

 18:50
18:50

 18:50
18:50
2025-09-18 18:34
 1:11
1:11

 1:11
1:11
2025-09-22 05:01

 11:47
11:47

 11:47
11:47
2025-09-15 14:52

 9:12
9:12

 9:12
9:12
2025-09-04 14:50

 13:06
13:06

 13:06
13:06
2025-09-19 03:50

 3:30
3:30

 3:30
3:30
2025-08-29 08:45
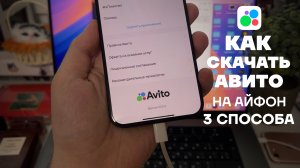
 2:39
2:39
![Зафар Эргашов - Мусофирда каридим (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 4:58
4:58
![MARSO - Дура (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:05
3:05
![Азимжон Сайфуллаев - Тупрок буламиз (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 4:38
4:38
![Артур Пирожков - ALARM (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:22
3:22
![Гор Мартиросян - 101 роза (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 4:26
4:26
![Фаррух Хамраев - Отажоним булсайди (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:08
3:08
![Жалолиддин Ахмадалиев - Тонг отгунча (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 4:44
4:44
![Рейсан Магомедкеримов - Забываю (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:20
3:20
![Виктория Качур - Одного тебя люблю (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:59
3:59
![Selena Gomez - In The Dark (Official Video 2025)]() 3:04
3:04
![Аля Вайш - По кругу (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:37
2:37
![Фати Царикаева - Стамбул (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:57
2:57
![Сергей Сухачёв - Розовый туман (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:13
3:13
![INSTASAMKA - AGENT GIRL (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:24
3:24
![5sta Family - Антидот (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:33
3:33
![Игорь Кибирев - Пьяная ночь (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:08
3:08
![Рустам Батербиев - Пора расстаться (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 2:38
2:38
![Светлана Ларионова - Осень отстой (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:30
3:30
![SERYABKINA, Брутто - Светофоры (Премьера клипа 2025)]() 3:49
3:49
![Anette - Erjanik em (Official Video 2025)]() 3:36
3:36
![Терминатор 2: Судный день | Terminator 2: Judgment Day (1991) (Гоблин)]() 2:36:13
2:36:13
![Никто 2 | Nobody 2 (2025)]() 1:29:27
1:29:27
![Французский любовник | French Lover (2025)]() 2:02:20
2:02:20
![Долгая прогулка | The Long Walk (2025)]() 1:48:08
1:48:08
![Только ты | All of You (2025)]() 1:38:22
1:38:22
![Молода и прекрасна | Jeune & jolie (2013)]() 1:33:24
1:33:24
![Супруги Роуз | The Roses (2025)]() 1:45:29
1:45:29
![Сверху вниз | Highest 2 Lowest (2025)]() 2:13:21
2:13:21
![Вечеринка только начинается | The Party's Just Beginning (2018)]() 1:31:20
1:31:20
![Лучшее Рождество! | Nativity! (2009)]() 1:46:00
1:46:00
![Школьный автобус | The Lost Bus (2025)]() 2:09:55
2:09:55
![Девушка из каюты №10 | The Woman in Cabin 10 (2025)]() 1:35:11
1:35:11
![Дикари | The Savages (2007)]() 1:54:19
1:54:19
![Пойман с поличным | Caught Stealing (2025)]() 1:46:45
1:46:45
![Положитесь на Пита | Lean on Pete (2017)]() 2:02:04
2:02:04
![Псы войны | Hounds of War (2024)]() 1:34:38
1:34:38
![Элис, дорогая | Alice, Darling (2022)]() 1:29:30
1:29:30
![Хищник | Predator (1987) (Гоблин)]() 1:46:40
1:46:40
![Богомол | Samagwi (2025)]() 1:53:29
1:53:29
![Эффект бабочки | The Butterfly Effect (2003)]() 1:53:35
1:53:35
![Сборники «Ну, погоди!»]() 1:10:01
1:10:01
![Котёнок Шмяк]() 11:04
11:04
![Ну, погоди! Каникулы]() 7:09
7:09
![Панда и петушок Лука]() 12:12
12:12
![Космический рейнджер Роджер Сезон 1]() 11:32
11:32
![Хвостатые песенки]() 7:00
7:00
![Агент 203]() 21:08
21:08
![Оранжевая корова]() 6:30
6:30
![Монсики]() 6:30
6:30
![Тёплая анимация | Новая авторская анимация Союзмультфильма]() 10:21
10:21
![Пип и Альба Сезон 1]() 11:02
11:02
![Зомби Дамб]() 5:14
5:14
![Корги по имени Моко. Новый питомец]() 3:28
3:28
![Сборники «Приключения Пети и Волка»]() 1:50:35
1:50:35
![Пиратская школа]() 11:06
11:06
![Врумиз. 1 сезон]() 13:10
13:10
![Псэмми. Пять детей и волшебство Сезон 1]() 12:17
12:17
![Таинственные золотые города]() 23:04
23:04
![МиниФорс]() 0:00
0:00
![Сборники «Простоквашино»]() 1:04:60
1:04:60

 2:39
2:39Скачать видео
| 256x144 | ||
| 640x360 | ||
| 1280x720 | ||
| 1920x1080 |
 4:58
4:58
2025-10-18 10:31
 3:05
3:05
2025-10-17 11:37
 4:38
4:38
2025-10-23 11:27
 3:22
3:22
2025-10-20 14:44
 4:26
4:26
2025-10-25 12:55
 3:08
3:08
2025-10-18 10:28
 4:44
4:44
2025-10-19 10:46
 3:20
3:20
2025-10-16 11:19
 3:59
3:59
2025-10-24 12:00
 3:04
3:04
2025-10-24 11:30
 2:37
2:37
2025-10-23 11:33
 2:57
2:57
2025-10-15 10:54
 3:13
3:13
2025-10-24 12:18
 3:24
3:24
2025-10-17 11:33
 3:33
3:33
2025-10-22 13:57
 3:08
3:08
2025-10-16 11:32
 2:38
2:38
2025-10-16 11:06
 3:30
3:30
2025-10-24 11:42
 3:49
3:49
2025-10-25 12:52
 3:36
3:36
2025-10-18 10:11
0/0
 2:36:13
2:36:13
2025-10-07 09:27
 1:29:27
1:29:27
2025-09-07 22:44
 2:02:20
2:02:20
2025-10-01 12:06
 1:48:08
1:48:08
2025-10-24 17:32
 1:38:22
1:38:22
2025-10-01 12:16
 1:33:24
1:33:24
2025-09-19 15:12
 1:45:29
1:45:29
2025-10-23 18:26
 2:13:21
2:13:21
2025-09-09 12:49
 1:31:20
1:31:20
2025-08-27 17:17
 1:46:00
1:46:00
2025-08-27 17:17
 2:09:55
2:09:55
2025-10-05 00:32
 1:35:11
1:35:11
2025-10-13 12:06
 1:54:19
1:54:19
2025-08-27 18:01
 1:46:45
1:46:45
2025-10-02 20:45
 2:02:04
2:02:04
2025-08-27 17:17
 1:34:38
1:34:38
2025-08-28 15:32
 1:29:30
1:29:30
2025-09-11 08:20
 1:46:40
1:46:40
2025-10-07 09:27
 1:53:29
1:53:29
2025-10-01 12:06
 1:53:35
1:53:35
2025-09-11 08:20
0/0
 1:10:01
1:10:01
2025-07-25 20:16
 11:04
11:04
2023-05-18 16:41
 7:09
7:09
2025-08-19 17:20
 12:12
12:12
2024-11-29 14:21
2021-09-22 21:49
 7:00
7:00
2025-06-01 11:15
 21:08
21:08
2025-01-09 16:39
 6:30
6:30
2022-03-31 18:49
 6:30
6:30
2022-03-29 19:16
 10:21
10:21
2025-09-11 10:05
2021-09-22 23:37
 5:14
5:14
2024-11-28 13:12
 3:28
3:28
2025-01-09 17:01
 1:50:35
1:50:35
2025-07-15 11:13
 11:06
11:06
2022-04-01 15:56
2021-09-24 16:00
2021-09-22 22:23
 23:04
23:04
2025-01-09 17:26
 0:00
0:00
2025-10-26 02:09
 1:04:60
1:04:60
2025-09-02 13:47
0/0